GASTRO INTESTINAL DISORDERS
Gastrointestinal conditions are disorders of the digestive system, an extensive and complex system that breaks down food in order to absorb water and extract nutrients, minerals and vitamins for the body’s use, while then removing unabsorbed waste .
Green life Therapies
When digestion is not happening properly, there will be an accumulation of undigested food in alimentary canal. At this stage you will get symptoms like anorexia, loss of appetite, nausea, belching, bloating, constipation, diarrhoea, vomiting, acidity, abdominal pain, bad breath, flatulence, etc. Accumulation of undigested materials will disturb the doshas, which can again disturb digestion. Gradually these accumulated residues turn toxic to body and start to generate diseases. Body will undergo more complex pathologies resulting into diseases like acid peptic disease, gluten intolerance, lactose intolerance, oesophageal reflux, Crohn’s disease, irritable bowel syndrome, celiac disease, ano rectal diseases like fistula-in-ano, chronic fissure, etc. Inefficient digestive energy is one of the primary causes of leaky gut.
- Abhyangam – Oil massage.
- Thakradhara – Stream of medicated buttermilk on your forehead.
- Virechanam – Purgation or laxative therapy.
- Vasthy – Enema therapy or infiltration of medicated oils per anus.
- Ksharasutra - Application of medicated thread in cases of fistula & piles
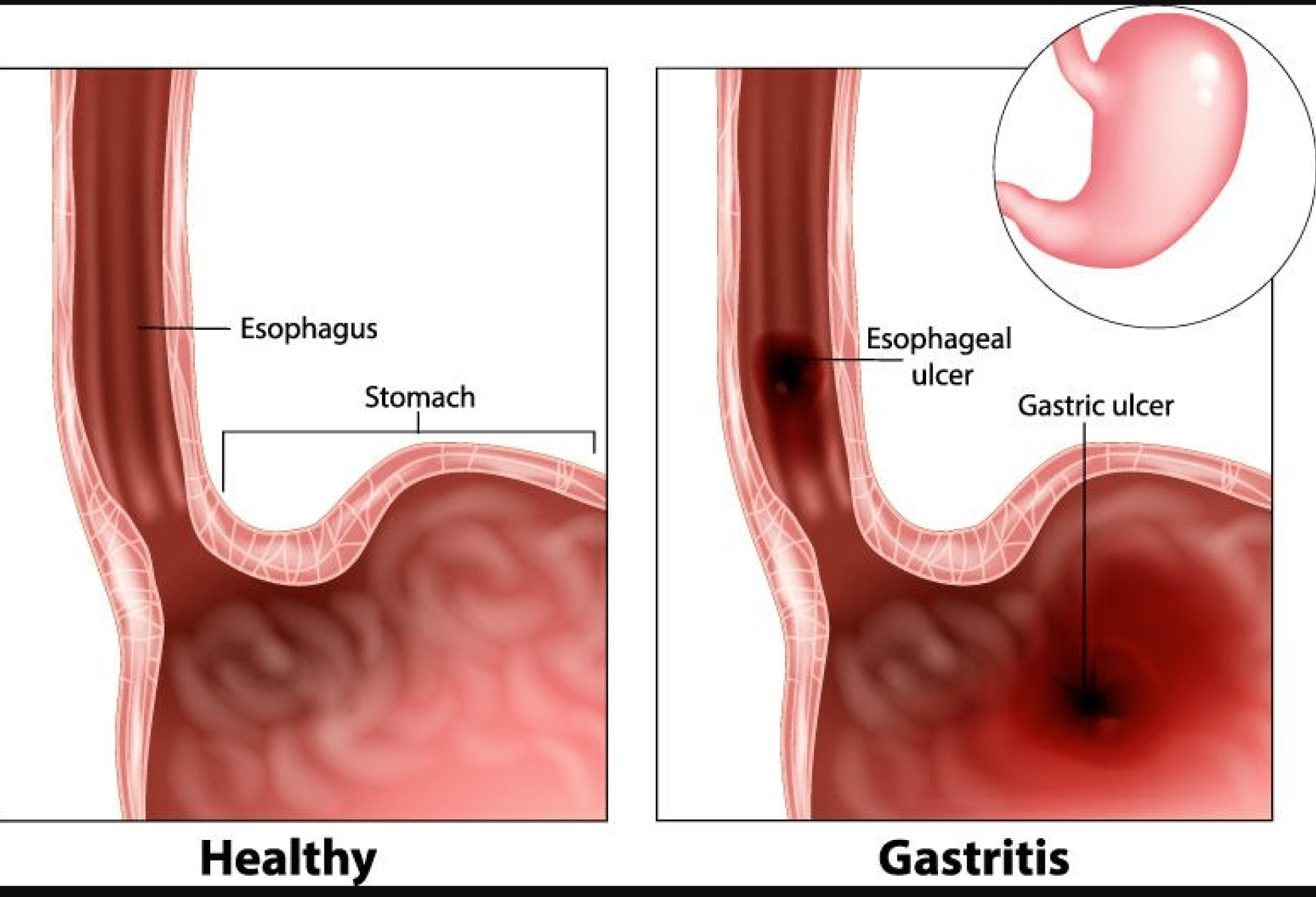 Gastritis is an inflammation, irritation, or erosion of the lining of the stomach. It can occur suddenly (acute) or gradually (chronic). Gastritis can be caused by irritation due to excessive alcohol use, chronic vomiting, stress, or the use of certain medications such as aspirin or other anti-inflammatory drugs.
Gastritis is an inflammation, irritation, or erosion of the lining of the stomach. It can occur suddenly (acute) or gradually (chronic). Gastritis can be caused by irritation due to excessive alcohol use, chronic vomiting, stress, or the use of certain medications such as aspirin or other anti-inflammatory drugs.
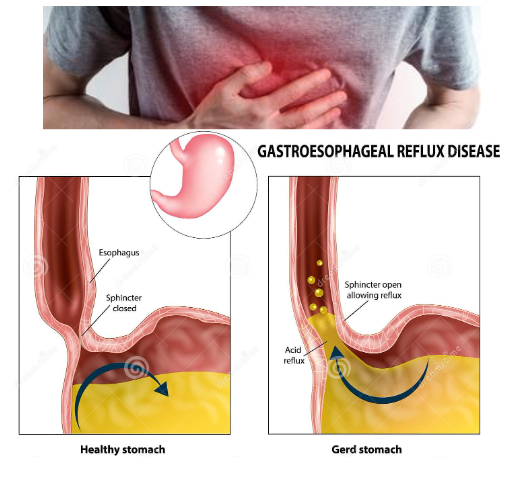 Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a digestive disorder that occurs when acidic stomach juices, or food and fluids back up from the stomach into the esophagus. GERD affects people of all ages—from infants to older adults.
People with asthma are at higher risk of developing GERD. Asthma flare-ups can cause the lower esophageal sphincter to relax, allowing stomach contents to flow back, or reflux, into the esophagus. Some asthma medications (especially theophylline) may worsen reflux symptoms.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a digestive disorder that occurs when acidic stomach juices, or food and fluids back up from the stomach into the esophagus. GERD affects people of all ages—from infants to older adults.
People with asthma are at higher risk of developing GERD. Asthma flare-ups can cause the lower esophageal sphincter to relax, allowing stomach contents to flow back, or reflux, into the esophagus. Some asthma medications (especially theophylline) may worsen reflux symptoms.
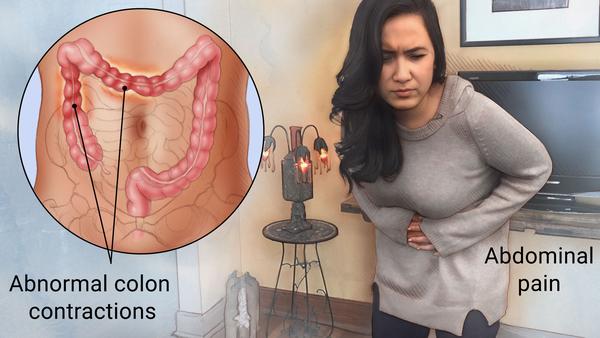 Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a common, long-term condition of the digestive system. Symptoms can include stomach cramps, bloating, diarrhoea and/or constipation. The condition is often lifelong, although the symptoms may change over time. With the right strategies, IBS can be successfully managed
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a common, long-term condition of the digestive system. Symptoms can include stomach cramps, bloating, diarrhoea and/or constipation. The condition is often lifelong, although the symptoms may change over time. With the right strategies, IBS can be successfully managed
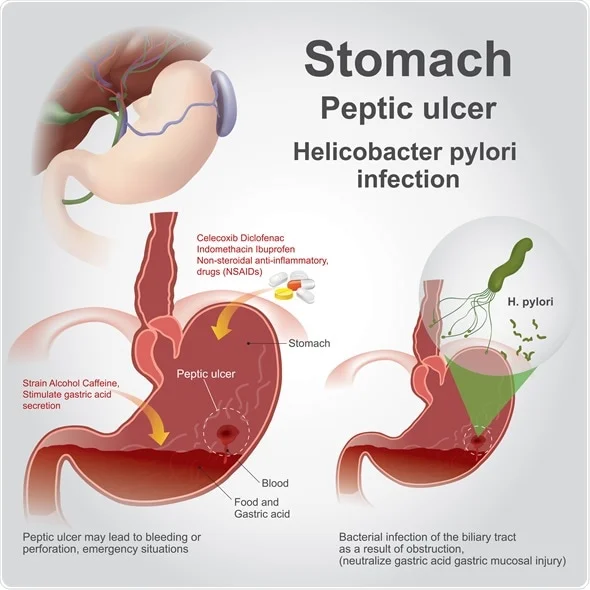 Peptic ulcer disease is a condition in which painful sores or ulcers develop in the lining of the stomach or the first part of the small intestine (the duodenum). Normally, a thick layer of mucus protects the stomach lining from the effect of its digestive juices. But many things can reduce this protective layer, allowing stomach acid to damage the tissue.
Peptic ulcer disease is a condition in which painful sores or ulcers develop in the lining of the stomach or the first part of the small intestine (the duodenum). Normally, a thick layer of mucus protects the stomach lining from the effect of its digestive juices. But many things can reduce this protective layer, allowing stomach acid to damage the tissue.
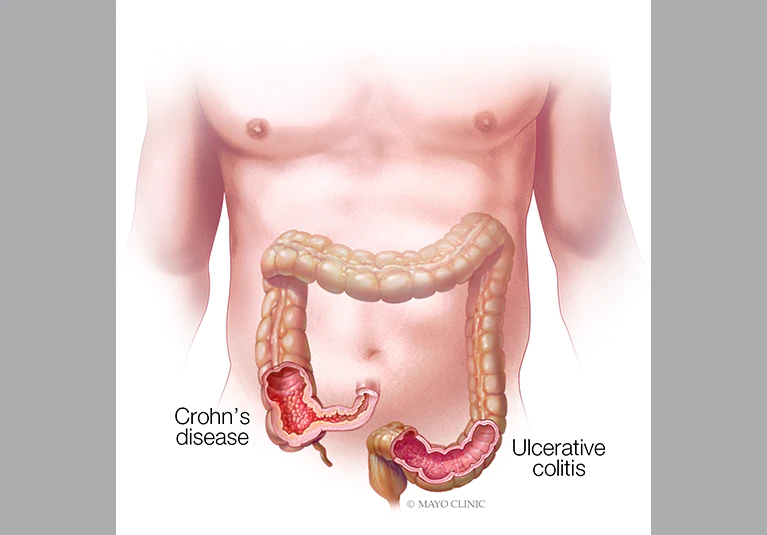 Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a term that describes disorders involving long-standing (chronic) inflammation of tissues in your digestive tract. Types of IBD include:Ulcerative colitis. This condition involves inflammation and sores (ulcers) along the lining of your large intestine (colon) and rectum.Crohn's disease. This type of IBD is characterized by inflammation of the lining of your digestive tract, which often can involve the deeper layers of the digestive tract. Crohn's disease most commonly affects the small intestine. However, it can also affect the large intestine and uncommonly, the upper gastrointestinal tract.
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a term that describes disorders involving long-standing (chronic) inflammation of tissues in your digestive tract. Types of IBD include:Ulcerative colitis. This condition involves inflammation and sores (ulcers) along the lining of your large intestine (colon) and rectum.Crohn's disease. This type of IBD is characterized by inflammation of the lining of your digestive tract, which often can involve the deeper layers of the digestive tract. Crohn's disease most commonly affects the small intestine. However, it can also affect the large intestine and uncommonly, the upper gastrointestinal tract.
 Constipation happens because your colon absorbs too much water from waste (stool/poop), which dries out the stool making it hard in consistency and difficult to push out of the body.
Constipation happens because your colon absorbs too much water from waste (stool/poop), which dries out the stool making it hard in consistency and difficult to push out of the body.To back up a bit, as food normally moves through the digestive tract, nutrients are absorbed. The partially digested food (waste) that remains moves from the small intestine to the large intestine, also called the colon. The colon absorbs water from this waste, which creates a solid matter called stool. If you have constipation, food may move too slowly through the digestive tract. This gives the colon more time – too much time – to absorb water from the waste. The stool becomes dry, hard, and difficult to push out.
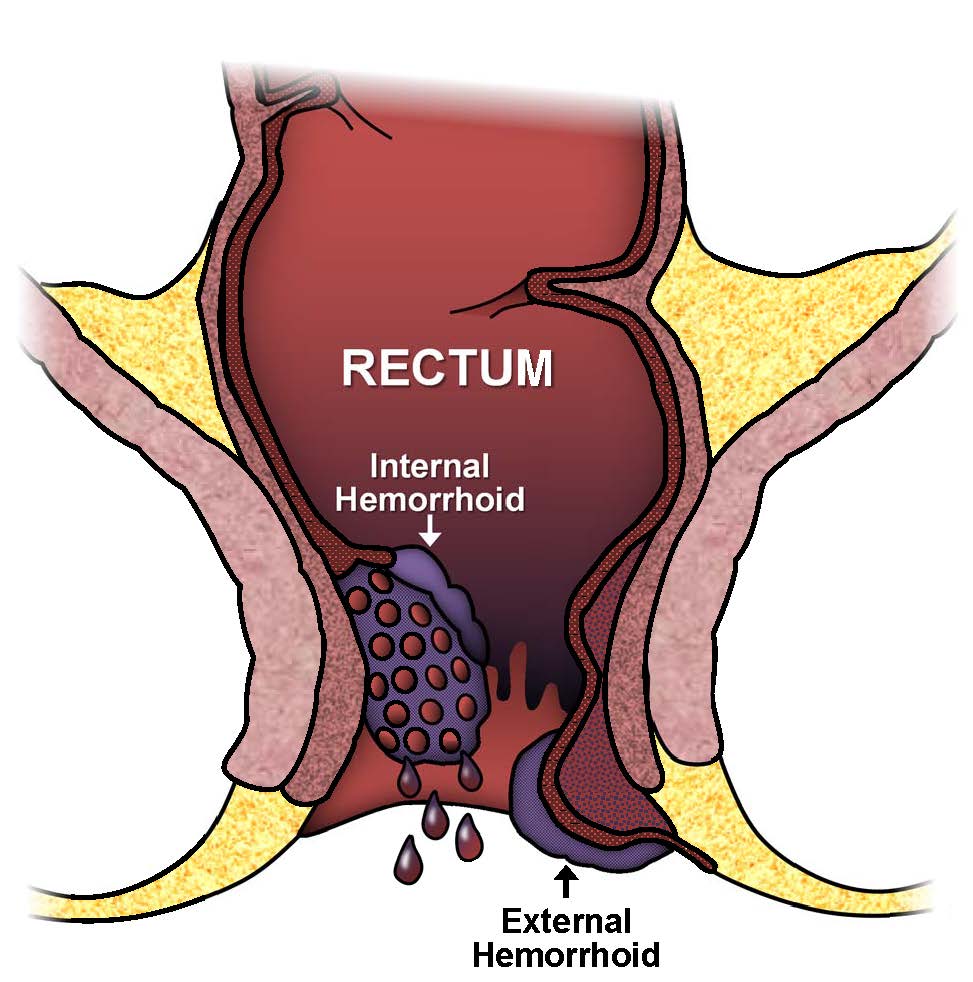 Hemorrhoids are swollen veins in the lowest part of your rectum and anus. Sometimes, the walls of these blood vessels stretch so thin that the veins bulge and get irritated, especially when you poop. Hemorrhoids are also called piles.Hemorrhoids are one of the most common causes of rectal bleeding
Hemorrhoids are swollen veins in the lowest part of your rectum and anus. Sometimes, the walls of these blood vessels stretch so thin that the veins bulge and get irritated, especially when you poop. Hemorrhoids are also called piles.Hemorrhoids are one of the most common causes of rectal bleeding
 An anal fistula is a small tunnel that connects an abscess, an infected cavity in the anus, to an opening on the skin around the anus.
An anal fistula is a small tunnel that connects an abscess, an infected cavity in the anus, to an opening on the skin around the anus.The anus is the external opening through which feces are expelled from the body. Just inside the anus are a number of small glands that make mucus. Occasionally, these glands get clogged and can become infected, leading to an abscess. About half of these abscesses may develop into a fistula.
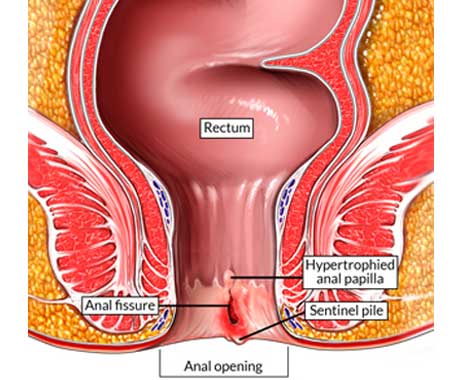 An anal fissure is a tear in the lining of the anus or anal canal (the opening through which stool passes out of the body). The fissure can be painful and may bleed.
An anal fissure is a tear in the lining of the anus or anal canal (the opening through which stool passes out of the body). The fissure can be painful and may bleed.
